The RICE Toolbox is a set of software tools for computing all rotational invariants of the cumulant expansion (RICE). Using representation theory, the RICE Toolbox enables the extraction of diffusion MRI cumulant tensors from arbitrary B-tensor encodings. We are sharing the software via Github and providing example datasets below.
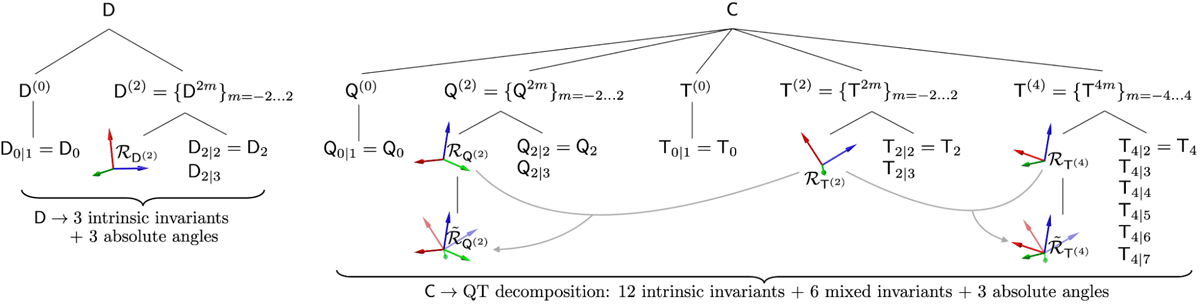
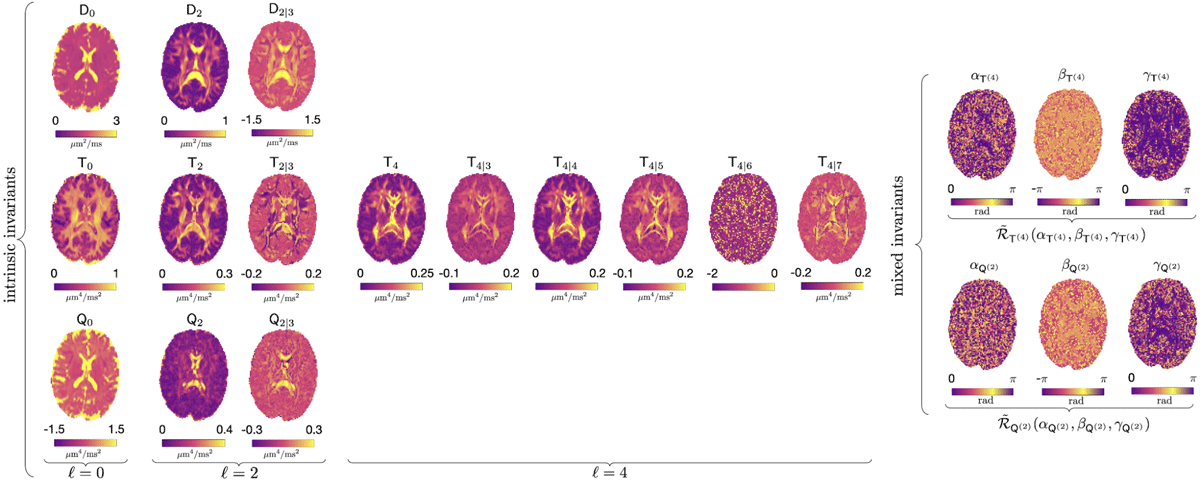
RICE describes the complete set of independent rotational invariants that can be formed from the cumulant tensors, thereby fully characterizing the diffusion MRI signal up to a given order, independent of the chosen basis or gradient waveform implementation. Owing to this invariance, RICE provides hardware- and protocol-independent descriptors with the potential to support robust diffusion MRI markers of development, pathology, and aging. In recent work that is currently under peer review we identify and construct a total of 21 such invariants at second order in the cumulant expansion, including 14 that have not previously been explored.
The RICE Toolbox, written in MATLAB, provides functions for parameter estimation of the O(b2) cumulant expansion (second order in b) for arbitrary axially symmetric b-tensors, including conventional pulsed gradient spin echo (PGSE) data. The framework can handle multiple variations of the cumulant expansion, such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), q-space trajectory imaging (QTI) and so on.
Related Preprint
Geometry of the cumulant series in neuroimaging.
Preprint posted online September 4, 2024; revised February 19 and August 22, 2025. arXiv:2409.03010 [physics.med-ph]
Please cite this preprint if you are using the RICE Toolbox in your research.
Get the Code
This resource is maintained on Github as RICE Toolbox (Rotational Invariants of the Cumulant Expansion).
Example Data
The example dataset consists of diffusion MRI data from a single subject, organized into four acquisition subsets. Each subset can be analyzed independently to demonstrate different capabilities of the RICE framework:
acq-lte-pte-fullRICE
Fully sampled linear and planar tensor encoding (LTE + PTE) data, enabling estimation of the complete set of RICE invariants.acq-lte-ste-iRICE
Minimal sampling of linear and spherical tensor encoding (LTE + STE), allowing fast estimation of mean diffusivity (MD), fractional anisotropy (FA), mean kurtosis (MK), and microscopic fractional anisotropy (µFA).acq-lte-fullDKI
Fully sampled LTE data suitable for estimating all conventional diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) invariants.acq-lte-iRICE
Minimally sampled LTE-only data for rapid estimation of MD, FA, and MK.
Get the Data
The data available on this page are provided free of charge and comes without any warranty. CAI²R and NYU Grossman School of Medicine do not take any liability for problems or damage of any kind resulting from the use of the files provided. Operation of the software is solely at the user’s own risk. The software developments provided are not medical products and must not be used for making diagnostic decisions.
The software is provided for non-commercial, academic use only. Usage or distribution of the software for commercial purpose is prohibited. All rights belong to the author (Santiago Coelho) and NYU Grossman School of Medicine. If you use the software for academic work, please give credit to the author in publications and cite the related publications.
Contact
Questions about this resource may be directed to Santiago Coelho, PhD, or Dmitry Novikov, PhD, or raised as issues on Github.
Related Story
Santiago Coelho, postdoctoral fellow who develops diffusion MRI methods for brain imaging, talks about modeling tissue properties, entering the field by chance, and what he proposes to do next.
Related Resource
Software for robust standard-model parameter estimation from diffusion MRI data.


