We are making available MATLAB code for radial diffusion spectrum imaging (RDSI) reconstruction.
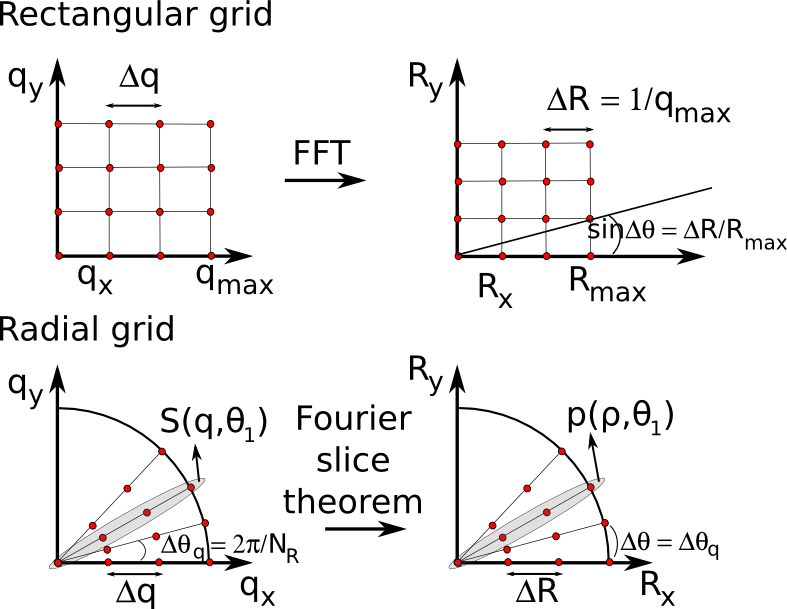
Diffusion spectrum imaging (DSI) has been shown to be an effective tool for noninvasively depicting the anatomical details of brain microstructure. Existing implementations of DSI sample the diffusion encoding space using a rectangular grid. Here we present a different implementation of DSI, named radial DSI or RDSI, in which a radially symmetric q-space sampling scheme for DSI results in improved angular resolution and accuracy of the reconstructed orientation distribution functions (ODFs).
RDSI combines radial q-space sampling with direct analytical reconstruction via the projection slice theorem—a combination that yields high-accuracy for in vivo DSI with good angular resolution at lower b-values. The robustness of this approach stems from calculating the ODF in the same angular direction in which the radial lines are sampled in q-space. RDSI and associated findings may have important implications for the design of DSI imaging protocols for clinical use.
For more information, see the related publications.
Related Publications
Radial q-space sampling for DSI.
Magn Reson Med. 2016 Sep;76(3):769-80. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25917
Accelerated radial diffusion spectrum imaging using a multi-echo stimulated echo diffusion sequence.
Magn Reson Med. 2018 Jan;79(1):306-316. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26682
Please cite these works if you are using RDSI reconstruction in your research.
Contact
Questions about this resource may be directed to Steven H. Baete, PhD.
